inchi-isotopologue-extension
Background Information:
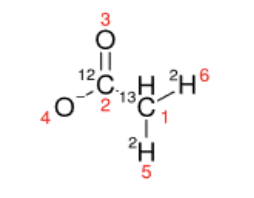
The current InChI specification contains an isotopic layer that can specify exact isotopomers. There is also some ability to specify limited atomic location ambiguity for hydrogen isotopes. For example, acetate containing one 13C and two 2H isotopes in the methyl group has the following InChI string:
InChI=1S/C2H4O2/c1-2(3)4/h1H3,(H,3,4)/p-1/i1+1D2,2+0
SMILES=[13CH]([12C](=O)[O-])([2H])[2H]
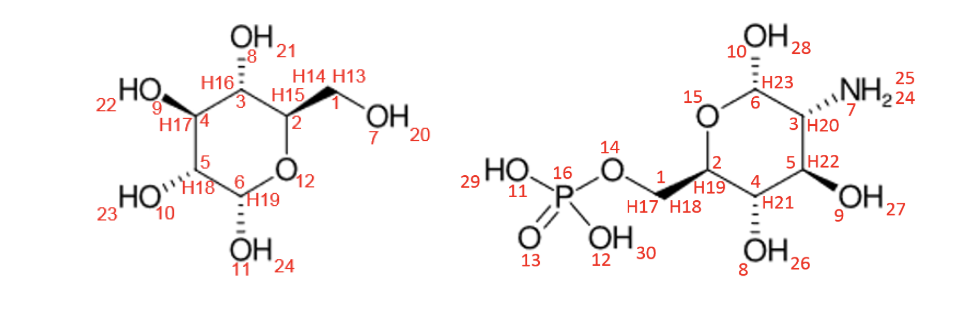
Here are example molecules we will use for demonstration in the following sections:
- alpha-D-glucopyranose (left)
InChI=1S/C6H12O6/c7-1-2-3(8)4(9)5(10)6(11)12-2/h2-11H,1H2/t2-,3-,4+,5-,6+/m1/s1
SMILES=C([C@@H]1[C@H]([C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H](O)O1)O)O)O)O
- 2-Amino-2-deoxy-6-O-phosphono-alpha-D-glucopyranose (right)
SMILES=C([C@@H]1[C@H]([C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H](O)O1)N)O)O)OP(=O)(O)O
InChI=1S/C6H14NO8P/c7-3-5(9)4(8)2(15-6(3)10)1-14-16(11,12)13/h2-6,8-10H,1,7H2,(H2,11,12,13)/t2-,3-,4-,5-,6+/m1/s1
Current InChI Isotopomer Specification:
-
Simple Definition:
/i#<+|->#[I#],.. -
Complete Definition:
/i<atom_number><isotope_designation>[<hydrogen_isotope><hydrogen_isotope_count>]
/i<atom_number>[<hydrogen_isotope><hydrogen_isotope_count>]
where:
* <atom_number> specific atom that has the specified isotope.
* `<isotope_designation>` isotope designation indicated by a sign (+ or -) and number indicating the unit mass difference from the rounded average atomic mass of the element.
For example, the average atomic mass of Sn (118.710) is rounded to 119 and the most abundant isotope <sup>120</sup>Sn is specified by “+1”.
* `<hydrogen_isotope>` D for deuterium. etc.
* `<hydrogen_isotope_count>` number of the specified hydrogen isotope bonded to the designated atom (`<atom_number>`); 1 if omitted.
-
Examples:
-
13C at carbons 1 and 2 in alpha-D-glucopyranose:
InChI=1S/C6H12O6/c7-1-2-3(8)4(9)5(10)6(11)12-2/h2-11H,1H2/t2-,3-,4+,5-,6+/m1/s1/i1+1,2+1 -
13C at carbon 1 with 2H2 attached in alpha-D-glucopyranose:
InChI=1S/C6H12O6/c7-1-2-3(8)4(9)5(10)6(11)12-2/h2-11H,1H2/t2-,3-,4+,5-,6+/m1/s1/i1+1D2 -
Carbon 1 with 2H2 attached in alpha-D-glucopyranose:
InChI=1S/C6H12O6/c7-1-2-3(8)4(9)5(10)6(11)12-2/h2-11H,1H2/t2-,3-,4+,5-,6+/m1/s1/i1D2 -
13C at carbon 1 with 2H1 attached in alpha-D-glucopyranose:
InChI=1S/C6H12O6/c7-1-2-3(8)4(9)5(10)6(11)12-2/h2-11H,1H2/t2-,3-,4+,5-,6+/m1/s1/i1D/t1?,2-,3-,4+,5-,6+Technically, this is an isotopologue fragment and not an isotopomer, meaning there is limited ambiguity in the location of the deuterium isotope.
-
2H bonded to carbon 1 in a stereospecific configuration in alpha-D-glucopyranose:
InChI=1S/C6H12O6/c7-1-2-3(8)4(9)5(10)6(11)12-2/h2-11H,1H2/t2-,3-,4+,5-,6+/m1/s1/i1D/t1-,2-,3-,4+,5-,6+This is a stereospecific isotopomer.
-
2H bonded to all heteroatoms of alpha-D-glucopyranose (as e.g. in exchange experiments):
InChI=1S/C6H12O6/c7-1-2-3(8)4(9)5(10)6(11)12-2/h2-11H,1H2/t2-,3-,4+,5-,6+/m1/s1/i7D,8D,9D,10D, 11D
-